Smart Automated Stress Testing System: Integrating Physical Characteristic Modeling Prediction and AI Visualization Analysis
This project developed a distributed automated stress testing system based on Golang, aimed at solving two major pain points of traditional testing tools: “difficulty in precisely controlling system wattage” and “difficulty interpreting massive data.”
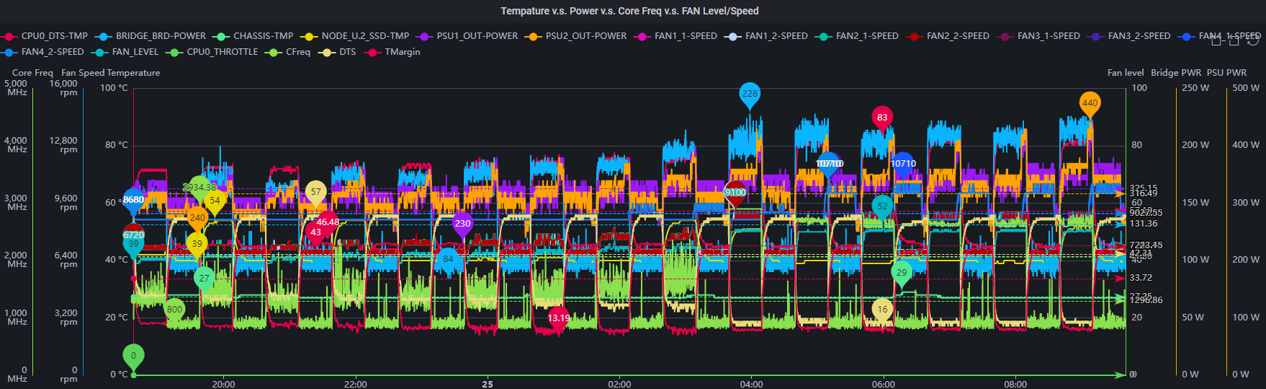
Unlike traditional tools that can only passively execute scripts, this system introduces physical characteristic modeling technology. By establishing specialized mathematical models for CPU (linear growth) and Memory/Ethernet (inverse exponential saturation) components, the system can reverse-engineer and precisely lock target stress environments. In data analysis, this system innovatively designed Grafana 4D heatmaps integrating temperature, RPM, wattage, and time frequency, and connects to AI visual models for automated chart interpretation. This solution successfully transformed system verification workflow from manual operation to Data-Driven intelligent decision-making mode, significantly improving test coverage and risk identification efficiency.
This project’s core technology includes two major breakthroughs:
Physical Characteristic Prediction Modeling: Established interpretable mathematical models for heterogeneous power consumption characteristics of CPU (linear growth) and Memory/Ethernet (inverse exponential saturation) components. Through linear fitting and algorithm reverse derivation, achieved precise control of system wattage and stress.
AI-Driven 4D Visualization: Innovatively designed Grafana 4D heatmaps integrating temperature, RPM, wattage, and time frequency, connected to visual AI models for automated chart interpretation, instantly identifying potential cooling risks and performance bottlenecks. This system successfully transformed hardware verification workflow from passive execution to proactive Data-Driven decision-making mode.
🛠️ Technical Case Study
1. System Architecture & Infrastructure
To meet large-scale testing requirements, this system adopts distributed architecture design:
- Agent Side (Golang CLI): Deployed on System Under Test (SUT), responsible for executing underlying test commands. Features local Log buffering mechanism ensuring data integrity even during network interruption.
- Controller Side: Provides one-to-many remote operation interface and reservation scheduling functionality for unattended testing.
- Monitoring & Analysis Side: Integrates Grafana for real-time monitoring and routes data streams to backend AI analysis modules.
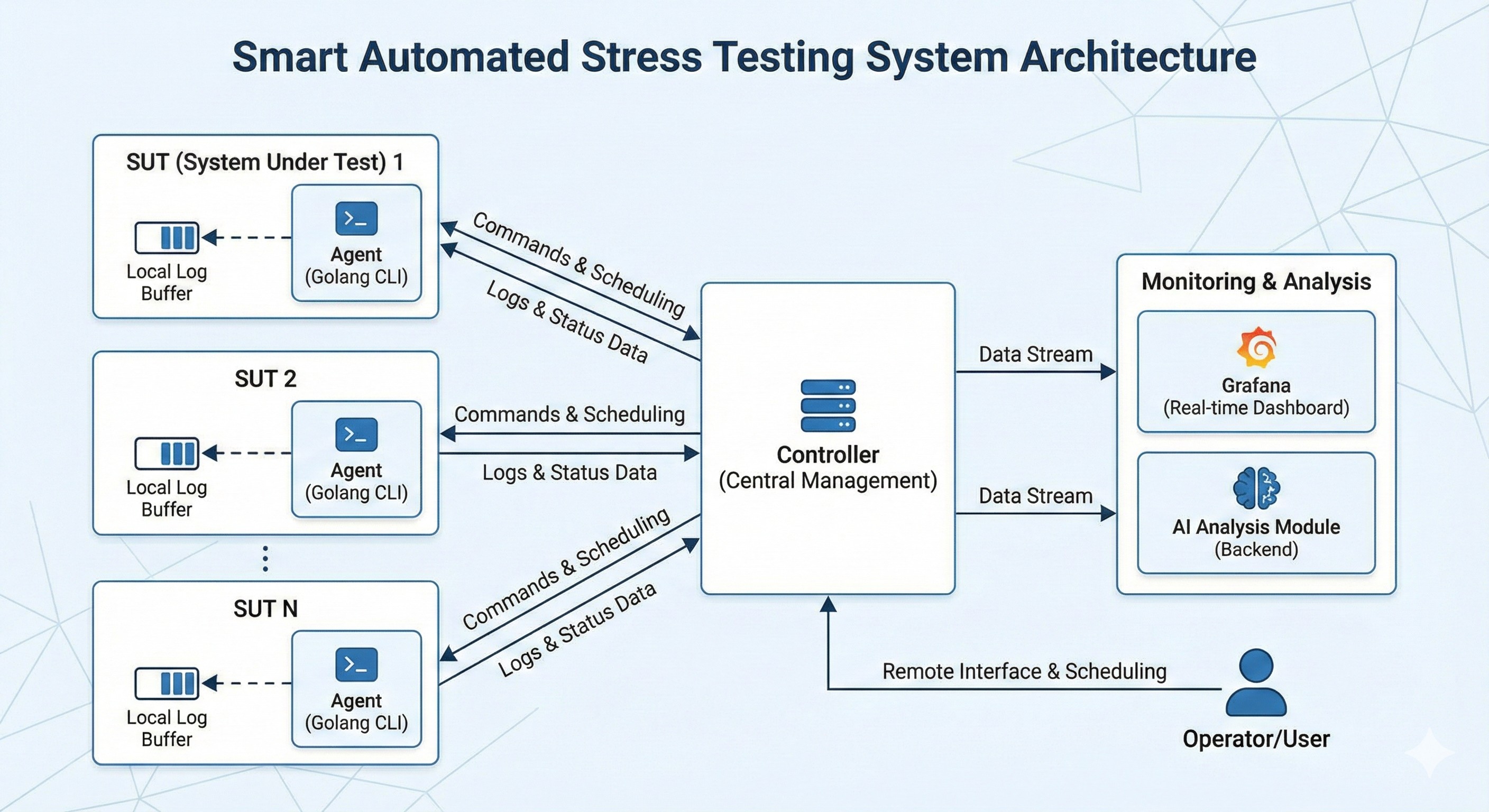
[Image placeholder: Recommend inserting System Diagram showing data flow between Agent, Controller, and AI Service]
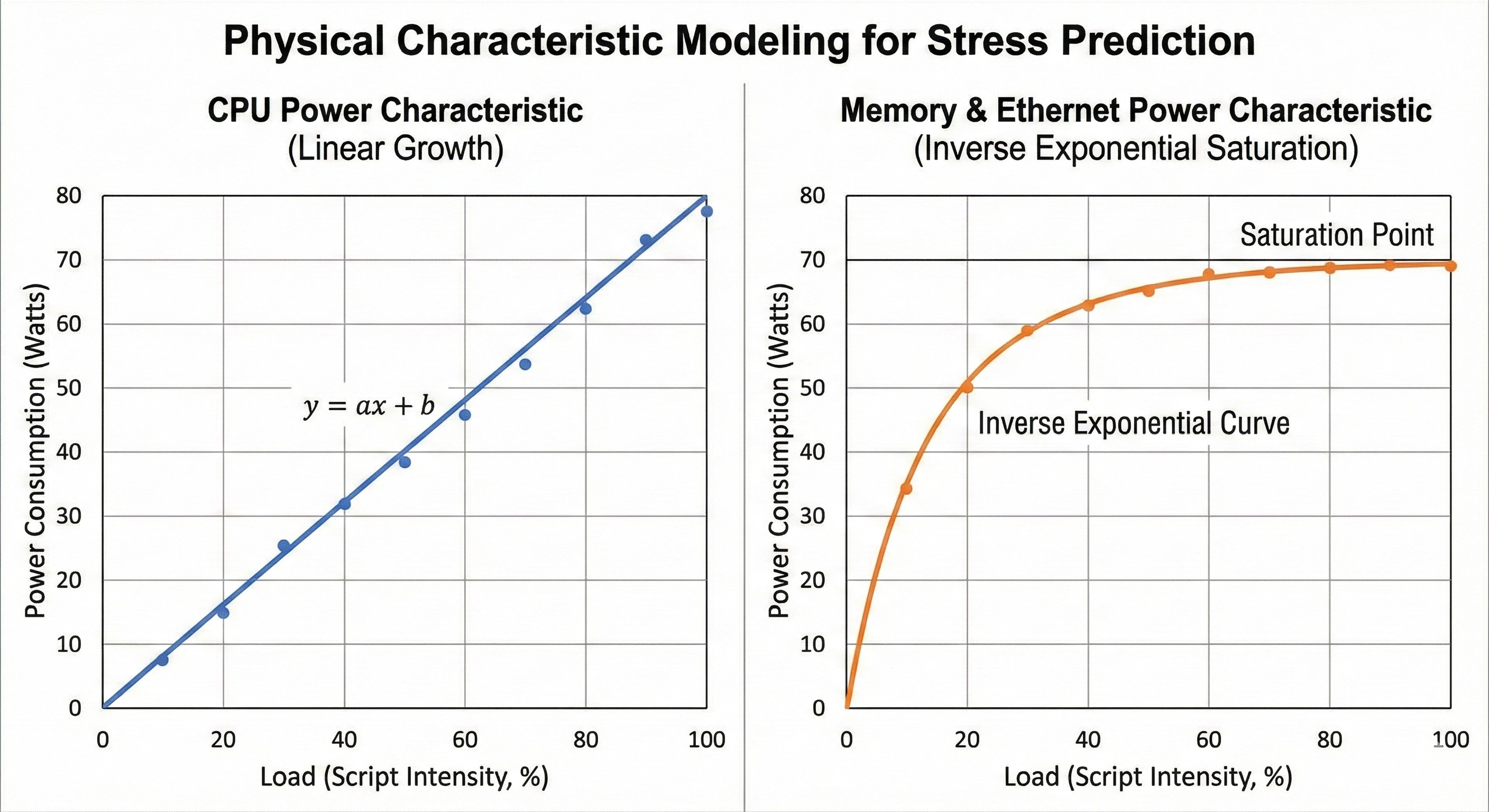
2. Core Technology: Physical Characteristic-Based Stress Prediction Model
This is the system’s most core intelligent engine. To precisely control systems reaching specific Thermal Design Power (TDP) boundaries, I abandoned traditional “trial-and-error” script adjustment methods and adopted mathematical modeling.
2.1 Physical Characteristic Discovery
By designing “Pre-test” processes to automatically scan each component’s response from light load to full load, I discovered significant physical differences in power consumption curves across components:
- CPU (Linear Growth): As load increases, wattage shows almost perfect linear rise ($y = ax + b$).
- Memory & Ethernet (Inverse Exponential Saturation): These components show rapid wattage increase during initial load increase, then level off approaching saturation point, exhibiting inverse exponential curve characteristics.
2.2 Mathematical Modeling & Precise Stress Application
Based on these discoveries, I manually derived interpretable mathematical formula models. When users input “target total wattage,” the system calculates through algorithms, considering each component’s weight and saturation characteristics, reverse-solving for optimal CPU, GPU, MEM, and IO script combination intensity.
3. Core Technology: 4D Data Visualization & AI Analysis
After solving the “control” problem, the next challenge is how to “interpret” complex data from long-duration testing.
3.1 Innovative 4D Grafana Heatmap
To present multi-variable system states on a 2D plane, I custom-designed Grafana panels integrating four dimensions of key information into one chart:
- X-axis: Temperature
- Y-axis: Fan Speed (RPM)
- Color: System Wattage (Power Consumption) - Intuitively shows load level through color intensity
- Point Size: Cumulative Duration/Frequency
Final Test Result Chart
4D Heatmap
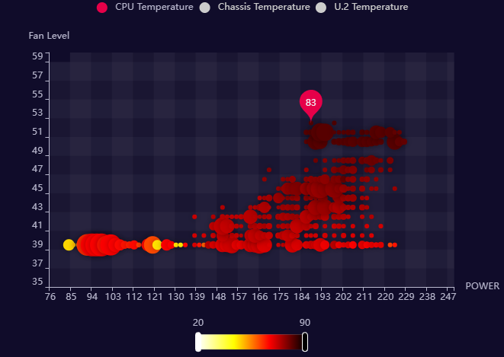
Data Visualization Chart